Kolb Learning Styles – 1976
David Kolb, the developer of Kolb Learning Styles, based his theory on the research of Jung, Rogers and even Piaget. The Kolb Learning Style Model is divided into four different styles which derive from a four stage learning cycle. This learning theory provides an understanding not just of individual learning styles based on the four quadrants but also explains a cycle of learning that can be applied to all learners. 
Kolb’s Four General Types and Learning Modes
Kolb’s Learning Styles are split into four general types including diverger, assimilator, converger and accommodator with two dimensions. The diverger learner is both concrete and reflective. These learners search for the answers to why and how. They learn best by observing and gathering information, avoiding conflict when possible.
An assimilator prefers the most logical course of action with their strength being thinking and reflecting over acting. Logic, organization and a strong sense of control are essential characteristics for assimilators. They benefit most when given time to reflect on new information.
Convergers also prefer to work alone but with their ideas. They search for well-defined tasks and learning by trial and error. This type of learner is an expert problem solver although they prefer to learn alone.
Lastly, accommodators are people oriented. They are the extrovert of the Kolb Learning Styles. Accommodators are action-oriented and task motivated. They are creative in their learning process taking risks while avoiding routine. Feeling and intuition have great value to these learners (McGill University, 2017; Pritchard, 2009).
Kolb (1984) continues his research to base learning on a cycle, proposing that learning occurs through experience. Within his theory, experiential learning possesses six attributes. First, learning is a process and not an end result. Second, learning is a continuous process through experience. Third, learning occurs when there are conflicts to be resolved within learning experiences. Fourth, “learning is an holistic process of adaptation to the world” (p31). Fifth, learning is a result of interaction between an individual and their environment. Sixth, learning is a process of creating knowledge through experiences.
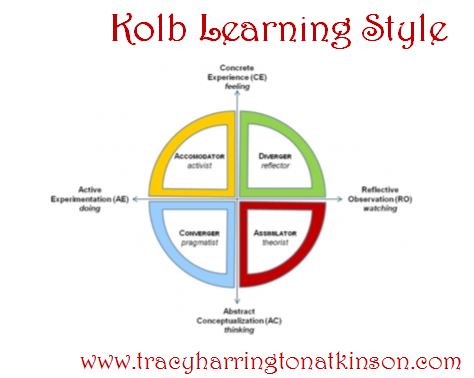
“Within the Kolb Learning Style Model four learning modes are identified: (1) Concrete Experience (CE), (2) Reflective Observation (RO), (3) Abstract Conceptualization (AC), and (4) Active Experimentation (AE).
“The Concrete Experience mode describes people who feel more than they think. Individuals inthis mode tend to be very good at relating to others and they tend to be intuitive decision-makers. The Reflective Observation mode describes people who would rather watch and observe others rather than be active participants. Individuals in this mode tend to appreciate exposure to differing points of view. The Abstract Conceptualization mode describes people who think more than they feel. Such people tend to have a scientific approach to problem solving as opposed to a more artistic approach. Finally, the Active Experimentation mode describes individuals who take an active role in influencing others as well as situations. These individuals welcome practical applications rather than reflective understanding as well as actively participating rather than observing” (Larkin-Hein, T. & Budny, D.B., 2017).
Kolb further stated that all four processes within the learning cycle had to be implemented in order for optimal learning to occur. Each mode of the learning cycle indicates one step toward the completion of the learning experience although learning was not linear and therefore could begin at any point in the cycle but wuold need to complete all four stages to complete the learning.
The concrete experience is associated with feeling. It may occur with a new experience or rediscovering an experience, but relates to people and being sensitive to others. The concrete experience leads the reflective observation or the visual aspect of the learner. In this stage a learner will begin a recognition of inconsistencies between their understanding and the experience through judgement and making observations from different perspectives. Abstract conceptualization is a reflection component, developing and designing a new idea or modifying an existing one. The last stage is the application or doing phase, entitled active experimentation where the learner applies the new knowledge and exhibits risk-taking.
Determining the Learning Style
To determine the learning style of an individual, the Kolb Learning Style Inventory needs to be completed. The results of this test identify one of the four learning style types – Accommodating, Assimilating, Converging and Diverging. A new version of this test also looks classifies learning into one of the newly discovered styles – initiating, experiencing, imagining, reflecting, analyzing, thinking, deciding, acting and balancing. A certified Kolb Learning Style Inventory report will assist in recognizing methods of personal learning effectiveness as well as assisting in guiding an individual in how to best use their learning style in work, personal and academic environments.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Kolb Learning Style
Kolb Learning Style has been lauded for diversity in that it approaches both a style of learning for individuals as well as the experience of learning. One is not confined to remain within a learning style and may find a change of style in learning situations as well as during the different stages of life. This theory addditionally postulates individuals may use different learning style approaches within different situations.
Roger Greenway (2004) effectively approached the varying weaknesses of the Kolb Learning Style beginning with the impact of the learning style within group situations where the learning may not be as effective when learners identify with the same learning style. Additionally experiential learning may not apply to all situations. There may be limited learning factors. “It doesn’t explain psychodynamic, social, and institutional aspects of learning.” Lastly, there exists controversy in the collection of data in the development of the theory suggesting a lack of range of cultures as well as objectivity, validity and reliability.
Sources:
Greenway, R. (2004) Experiential Learning: articles and critiques of David Kolb’s theory Available online at: reviewing.co.uk/research/experiential.learning.htm
Kolb, D.A. (1984). Experiential Learning: Experience as the Source of Learning and Development. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Larkin-Hein, T. & Budny, D.B. (2017). Why Bother Learning about Learning Styles and Psychological Types? American University: Washington, DC. University of Pittsburgh: Pittsburgh, PA. Retrieved from http://fs2.american.edu/tlarkin/www/pdf_files/Session3280P&EP.PDF
McGill University. (2017). Learning Styles. Retrieved from https://www.mcgill.ca/thewelloffice/resources/yourwellness/academic/learning-styles
Pritchard, A. (2009). Ways of learning: Learning theories and learning styles in the classroom (2nd ed.). New York, NY:Routledge.
University of London. (2017). What is Learning from Experience. Retrieved from http://www.learningexperience.org.uk/what-is-learning-from-experience/
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel by clicking here.
Tracy Atkinson, mother of six, lives in the Midwest with her husband and spirited long-haired miniature dachshunds. She is a teacher, having taught elementary school to higher education, holding degrees in elementary education and a master’s in higher education. Her passion is researching, studying and investigating the attributes related to self-directed learners and learning styles. She has published several titles, including MBTI Learning Styles: A Practical Approach, The Art of Learning Journals, Calais: The Annals of the Hidden, Lemosa: The Annals of the Hidden, Book Two, Rachel’s 8 and Securing Your Tent. She is currently working on a non-fiction text exploring the attributes of self-directed learners: The Five Characteristics of Self-directed Learners. Check out her courses on Udemy.
arners.


Comments are closed