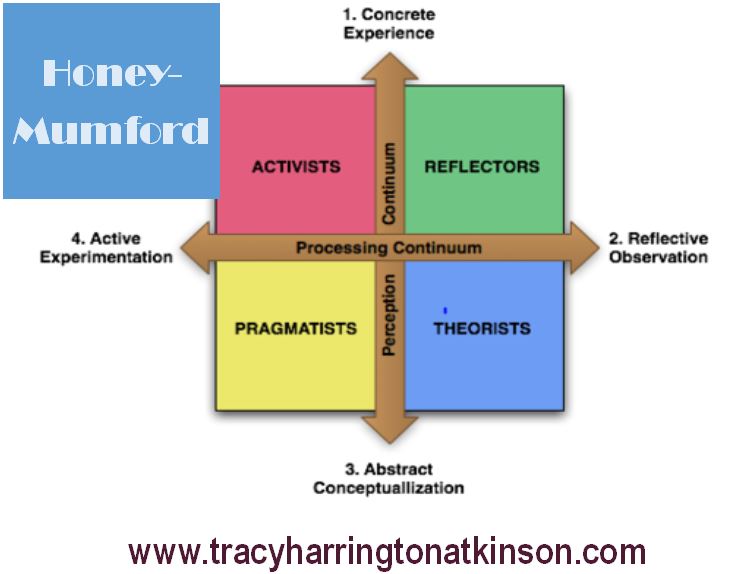
 Another cognitive learning theory is the Honey-Mumford model which is founded by Peter Honey and Alan Mumford. They based their initial work from the Kolb Learning Style to discover four specific styles namely activists, reflectors, theorists and pragmatists. Each type possesses unique characteristics which when understood can enhance the learning experience. Activists particularly enjoy learning by doing. They are experiential learners who will try anything, prefer to work in groups and generally require little to no planning. Reflectors are more reserved than the activists as they prefer to be data collectors and observers. This style will be slower to decide. The theorist may also be slow to decide as they need to be well-organized and tidy. They are especially methodical and logical as they adapt new information into old frameworks. Lastly, pragmatists are the practical applicators. They seek out problem solving opportunities to utilize new information (Pritchard, 2009).
Another cognitive learning theory is the Honey-Mumford model which is founded by Peter Honey and Alan Mumford. They based their initial work from the Kolb Learning Style to discover four specific styles namely activists, reflectors, theorists and pragmatists. Each type possesses unique characteristics which when understood can enhance the learning experience. Activists particularly enjoy learning by doing. They are experiential learners who will try anything, prefer to work in groups and generally require little to no planning. Reflectors are more reserved than the activists as they prefer to be data collectors and observers. This style will be slower to decide. The theorist may also be slow to decide as they need to be well-organized and tidy. They are especially methodical and logical as they adapt new information into old frameworks. Lastly, pragmatists are the practical applicators. They seek out problem solving opportunities to utilize new information (Pritchard, 2009).
Honey and Mumford determined that individuals have natural tendencies toward one learning style or another; yet, learners can expand and push outwards to develop additional forms of learning. In order to maximize each learning experience, an individual needs to know their style of learning and look for opportunities to use that style within each opportunity. Additionally, an increased awareness to one’s learning style encourages circumstances for self-reflection and improvement for more learning experiences and different learning situations.
Damrongpanit and Reungtragul (2013) share an interesting disadvantage to Honey-Mumford which can be applied to all learning theories. As an individual learns about their personal preferences, they can become too dependent upon them and avoid situations which would cause them to stretch and grow beyond their comfort zones. Particularly to the Honey-Mumford, these researchers state the implications of using qualitative information to design a learning theory with little to no quantitative evidence. Lastly, some researchers (Hayes & Allinson, 1988) debate the concrete ideas within the Honey-Mumford learning style, finding learning preferences may simply be indicative of one’s culture and race.

Click on image for pdf.
One of the greatest advantages to the Honey-Mumford styles is the simply ability for a student to have a better understanding of themselves and their learning styles. Individuals possess a greater capacity to profit from learning opportunities as they adjust to the unique situations with which the new information is embedded. Additionally, Honey-Mumford helps instructors to recognize their preferred learning style which tends to bleed into their teaching style, becoming the predominant instructional method. Another significant benefit to the Honey-Mumford is the 80 item questionnaire which provides individuals with a ranking of their learning personalities.
References
Damrongpanit, S. & Reungtragul, A. (2013). Matching of learning styles and teaching styles: Advantage and disadvantage on ninth-grade students’ academic achievements. Educational Research and Reviews, 8(20), 1937-1947.
Hayes, J & Allinson, C.W. (1988). Cultural differences in learning styles of managers. International Management Review, 28, 75-80.
Pritchard, A. (2009). Ways of learning: Learning theories and learning styles in the classroom (2nd ed.). New York, NY:Routledge.
By Tracy Atkinson
Tracy Atkinson, mother of six, lives in the Midwest with her husband. She is a teacher, having taught elementary school to higher education, holding degrees in elementary education and a master’s in higher education. Her passion is researching, studying and investigating the attributes related to self-directed learners. She has published several titles, including Calais: The Annals of the Hidden, Lemosa: The Annals of the Hidden, Book Two, Rachel’s 8 and Securing Your Tent. She is currently working on a non-fiction text exploring the attributes of self-directed learners: The Five Characteristics of Self-directed Learners.
Comments are closed