In the quest to understand how individuals learn and process information, researchers have developed various models and inventories. One such prominent framework is Vermunt’s Inventory of Learning Styles, which offers insights into how different learning preferences impact educational experiences. This model is particularly useful for educators, students, and professionals seeking to enhance their learning strategies and teaching methodologies.
What is Vermunt’s Inventory of Learning Styles?
The Inventory of Learning Styles (ILS) identifies four distinct learning styles based on the ways individuals approach learning tasks. These styles are derived from the cognitive, metacognitive, and affective dimensions of learning. Vermunt’s model emphasizes that learning is not a one-size-fits-all process and that recognizing individual differences can lead to more effective learning experiences.
The Four Learning Styles
Vermunt’s Inventory categorizes learning styles into four main types:
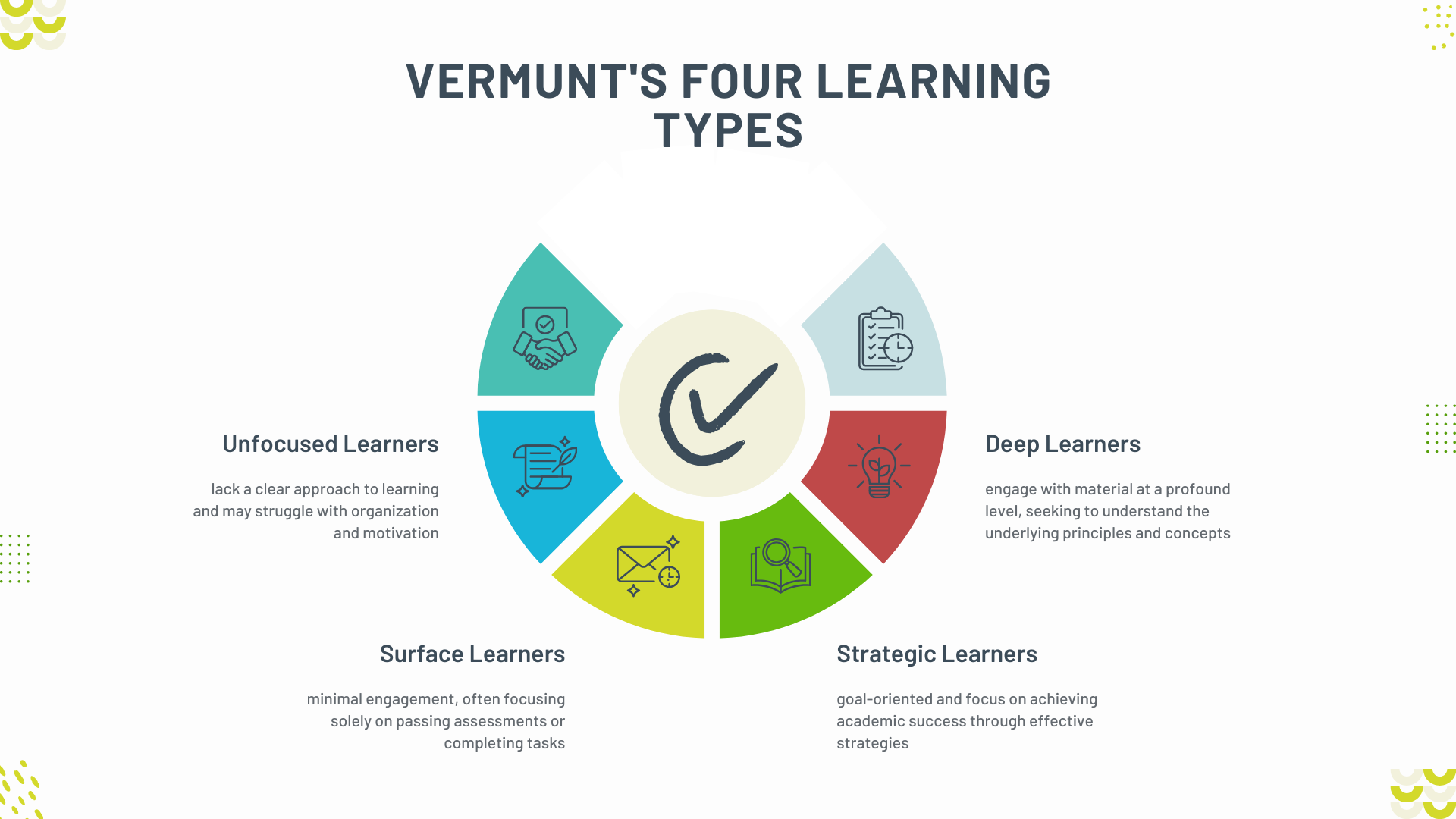
- Deep Learners:
- Characteristics: Deep learners engage with material at a profound level, seeking to understand the underlying principles and concepts. They are motivated by a desire to learn and value intrinsic understanding over rote memorization.
- Approach to Learning: These learners often employ critical thinking, reflection, and a thorough analysis of information. They relate new knowledge to prior experiences, aiming for a holistic understanding of the subject matter.
- Ideal Learning Environment: Environments that promote discussion, critical inquiry, and opportunities for exploration resonate well with deep learners.
- Strategic Learners:
- Characteristics: Strategic learners are goal-oriented and focus on achieving academic success through effective strategies. They employ various techniques to organize, monitor, and evaluate their learning processes.
- Approach to Learning: These learners are adept at selecting study methods that align with their objectives. They often use time management, planning, and self-regulation to maximize their learning outcomes.
- Ideal Learning Environment: Structured environments that provide clear goals, assessments, and feedback are ideal for strategic learners.
- Surface Learners:
- Characteristics: Surface learners tend to approach learning with minimal engagement, often focusing solely on passing assessments or completing tasks. They may rely on memorization without seeking deeper understanding.
- Approach to Learning: This style often involves a focus on factual recall and rote learning. Surface learners may feel overwhelmed by complex material, leading them to disengage from the learning process.
- Ideal Learning Environment: Environments that offer clear guidelines and straightforward tasks can help surface learners succeed, but they may benefit from encouragement to explore deeper learning strategies.
- Unfocused Learners:
- Characteristics: Unfocused learners lack a clear approach to learning and may struggle with organization and motivation. They often feel uncertain about their goals and may switch between different strategies without consistency.
- Approach to Learning: This group may exhibit disinterest or frustration, leading to erratic learning patterns. Unfocused learners often benefit from guidance and support in developing effective study habits.
- Ideal Learning Environment: Supportive environments that provide structure, encouragement, and mentorship can help unfocused learners find direction in their studies.
Conclusion
Vermunt’s Inventory of Learning Styles provides valuable insights into the diverse ways individuals approach learning. By recognizing and embracing these differences, educators and learners can create a more effective and inclusive educational experience. Understanding one’s learning style not only enhances academic performance but also empowers individuals to become lifelong learners, adaptable in various contexts. As we continue to explore the intricacies of learning, Vermunt’s model remains a crucial tool in fostering growth and success in education.

Comments are closed